Do your students struggle to understand exponents and roots? Does this present a challenge when solving order of operation problems? Keep reading to discover strategies to use as you teach.
#1 – Exponents and Roots: What are Common Errors?
First, consider the most common errors in student work with exponents and roots.
1. Students interpret a number cubed as a number times three.
2. Students interpret the root sign as division.

Secondary to these common errors, I recommend hands-on and visual strategies. If students can see it, they can do it.
#2 – Strategies
A. Hands-On Strategy for Introducing Exponents and Roots
Furthermore, let’s begin with a hands-on strategy that helps students visualize squared numbers. Introduce by using an example with tiles or other similar manipulatives. See the example below.
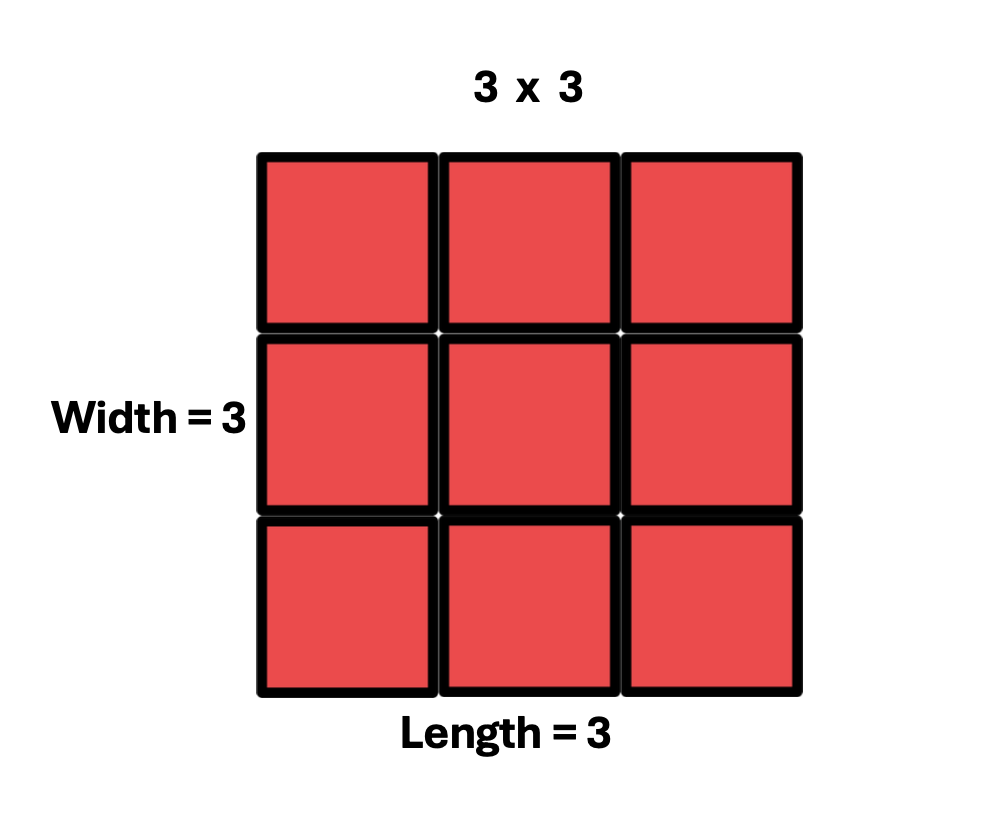
Image credit:
https://www.teacherspayteachers.com/browse?search=bunny%20on%20a%20cloud
1. First, explain the meaning of a number squared, using nine tiles with three rows and three columns to create a square.
2. Second, emphasize the length times the width represents a total number of 9 tiles.
3. Third, provide time for students to illustrate, and calculate other squared numbers
For example, a 4 x 4 arrangement will result in 16 tiles altogether.
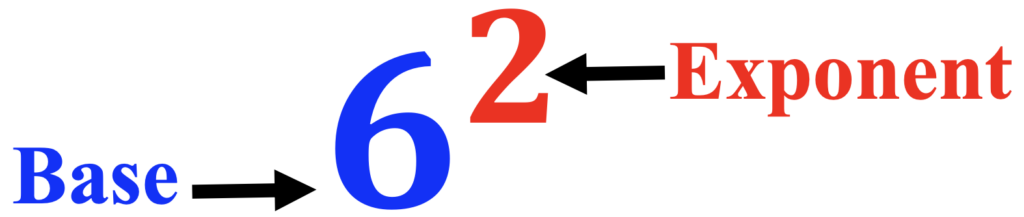
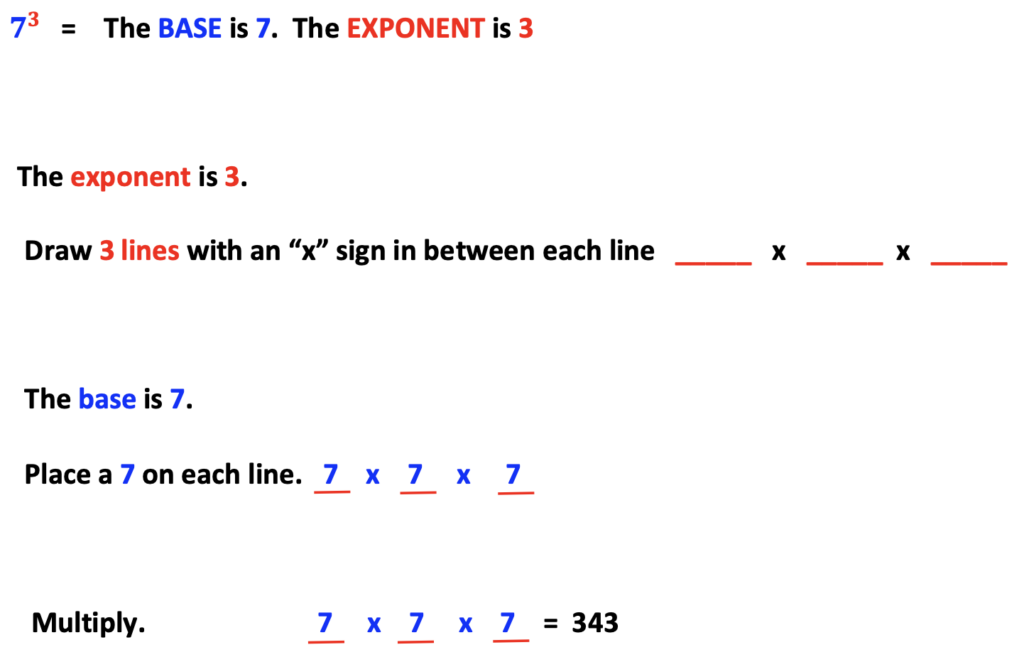
B. The Base and Exponent
Next, introduce a number with an exponent. Color-code the base and the exponent. I like to use blue for the base and red for the exponent. This allows students to make color-word associations such as blue base, red exponent, such as an exit sign that is red and white.
C. Roots
Now, introduce roots. Color – code the symbol green and the index, red. Red is used again to help students see the relationship between the index number and the exponent value.
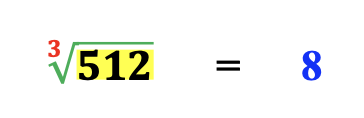
D. Reference Page
Also, provide a quick reference page. Place the list on a bulletin board. Provide students with a page to place in their binder, such as the one listed below.

Furthermore, as students observe values on the reference page, point out examples that “contain” the answer.
For example, let’s consider the number, 8 cubed. Add all the digits 5, 1, and 2 together. The result is 8. Encourage students to look for other patterns and relationships.
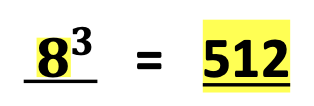
#3 – Emphasize Exponents and Roots Using Lines
Likewise, visualize exponents and roots by using lines.
Next, observe the number 512 with a root of 3. The answer is 8, meaning 8 x 8 x 8 = 512.
Also, notice three lines are provided to remind students to multiply “8” three times.
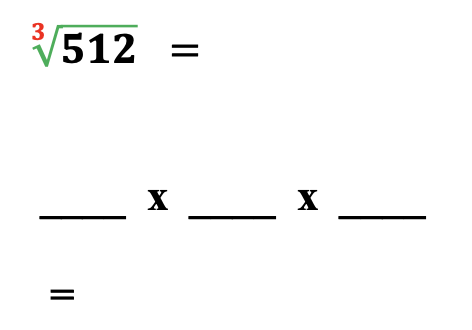
#4 – Student: “How Do I ask a Question?”
In addition, there are students with questions. Due to the complex terminology, they struggle with constructing words to ask questions.

Next, help students understand that exponents are opposites of roots. Use this concept to help students use accurate terminology. For class practice, write color-coded sentences using the terminology as written below.

Conclusion
Concepts related to the exponent and root is an important topic that provides student success with order of operations and other advanced math topics. Build student confidence with exponents and roots using hands-on strategies and highly visual examples. This will lead to success with exponent and root problems.
If you are looking for a resource that includes examples provided in this post, click on the link below the image to learn more.

Other Related Posts
Looking for More Materials?
Click the button below to view more of my educational resources!
