
Introduction
Are your students struggling with fraction operations which include mixed numbers in the operation? When you review their work do you notice steps get mixed up with other operations? You may have encountered multiplication problems where students have attempted to find the least common denominator. No problem. In this blog it is my passion to provide strategies to successfully teach fraction operations with mixed numbers. I’ve got your back!
You may also be interested in the blog, “How to Teach Fraction Operations” (with proper and improper fractions) Click the link below: https://ledtodiscover.com/middle/how-to-successfully-teach-fraction-operations/
- Contents
Introduction
1. Preparation to Succeed with Mixed Numbers
General Fraction Preparation
2. Types of Fractions
Three Types
How to Convert Between Mixed Numbers and Improper Fractions
3. How to Add and Subtract Fractions with Like Denominators and Two Mixed Numbers
4. How to Add, Subtract, Multiply and Divide Fractions with a Mixed and Whole Number
Add a Mixed Number to a Whole Number
Multiply a Mixed Number Times a Whole Number
Divide a Mixed Number by a Whole Number
5. How to Add, Subtract, Multiply and Divide Fractions with a Mixed Number and Proper Fraction
Add with like denominators
Subtract with like denominators
Multiply
Divide
Add with Unlike Denominators
6. How to Multiply and Divide Fractions with Two Mixed Numbers
Multiply
Divide
7. How to Add and Subtract Fractions with Unlike Denominators and Two Mixed Numbers
Add
Subtract
Conclusion
1. Preparation to Succeed with Mixed Numbers
General Fraction Preparation
Student success with fractions is associated with confidence in basic math skills such as memorized multiplication facts, listing factors of numbers, and the ability to see relationships between numbers, which is referred to as number sense. In relation to fractions, these basic skills are a foundation for other skills such as finding the greatest common factor for reducing fractions and finding the least common multiple for adding and subtracting fractions with unlike denominators. Students with these skills will be equipped and confident as you successfully teach fraction operations with mixed numbers.
2. Types of Fractions
Three Types
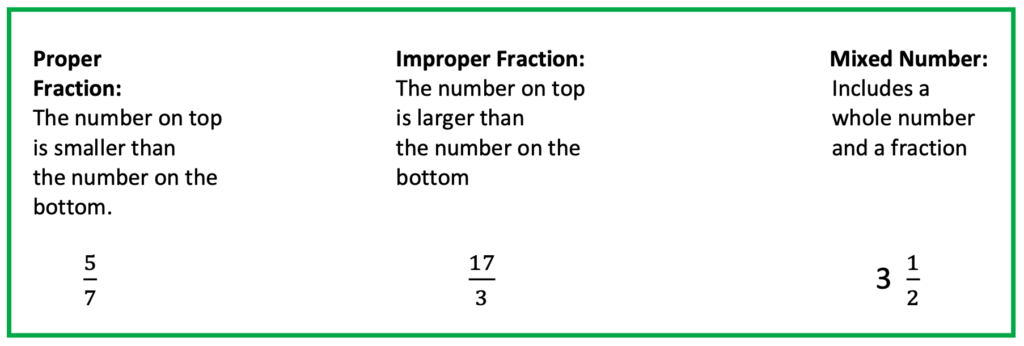
How to Convert Between Mixed Numbers and Improper Fractions


3. How to Add and Subtract Fractions with Like Denominators and Two Mixed Numbers
This is an ideal place to start fraction operations with mixed numbers. Visual and hands-on, examples can be used to illustrate fraction operations with like denominators.


4. How to Add, Subtract, Multiply, and Divide Fractions with a Mixed and Whole Number
Do you have students with difficulty visualizing and organizing their written work on paper? If so, this next step will be helpful when solving fraction operations with mixed numbers. When there is a whole number in a fraction operation, I always instruct my students to change the whole number into a proper fraction by writing the whole number over the number, 1. For example, 9 = 9/1.
Also, if students demonstrate difficulty visualizing and organizing their work, use of enlarged graph paper is also helpful.
As used in each of the following examples, you will notice that parts of each section is color-coded. This allows students to visually focus on a specific step being completed. The use of color is like magic for many students.




5. How to Add, Subtract, Multiply, and Divide Fractions with a Mixed Number and Proper Fraction





6. How to Multiply and Divide Fractions with Two Mixed Numbers


7. How to Add and Subtract Fractions with Unlike Denominators and Two Mixed Numbers


Conclusion
Solving fractions with mixed numbers requires all steps used with other types of fraction operations. The key difference: working with mixed numbers requires changing the mixed number into an improper fraction. For example, 2 3/4 = 11/4. Also, when working with whole numbers, the whole number is placed over the number, 1. For example, 9 = 9/1.
In Review: The Basic Steps for Solving Fractions with Mixed Numbers:
1. Change all whole or mixed numbers to improper fractions.
2. Solve the specific steps for each type of fraction operation.
For example, when adding fractions with like denominators, add the numbers in the numerator, keep the number in the denominator.
3. If the answer results in an improper fraction, change it to a mixed number.
4. If needed, reduce the fraction to lowest terms.
To keep these skills intact, review the methods for fraction operations with mixed numbers to the end of the school year.
Practice makes better!
